Getting started
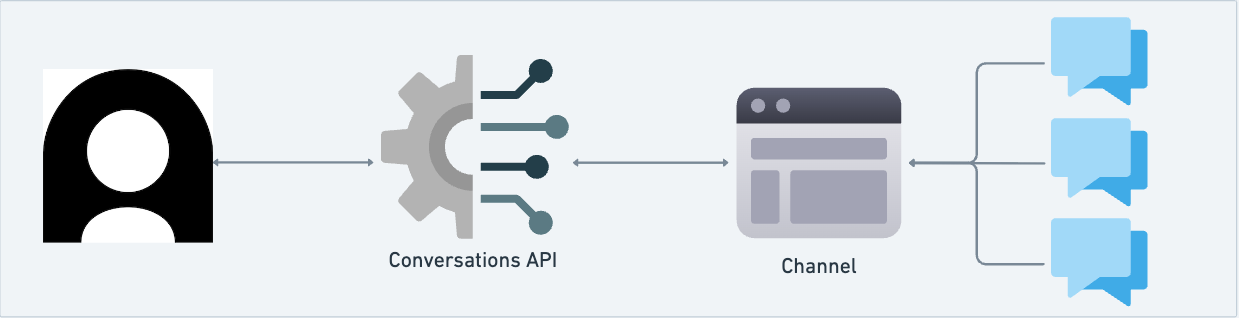
Who is this for?
The Conversations API is designed for developers and technical teams who want to extend Ada beyond its native channels. Typical users include teams that need to:
- Build and manage their own messaging frontends
- Integrate Ada with an existing email provider
- Connect Ada to third-party platforms or proprietary systems not supported out of the box
Implementation example
To see a working implementation of a frontend that interacts with an Ada AI Agent via the Conversations API, visit our public repository for complete details: ada-conversations-api-demo.
Core concepts
Now that you know what the Conversations API does and who it serves, let’s explore its key principles. At a high level, the API is organized around a few main concepts:
-
Channel: A communication pathway through which customers interact with your business. For custom channels, you create a new channel with a
messagingoremailmodality.The
emailmodality for custom channels is not the same as Ada’s native Email channel, which is accessed through the Email Conversations API. -
Conversation: A sequence of messages exchanged between participants on a specific channel. Participants can include the end user, the AI Agent, and human agents.
-
Message: A unit of communication authored by a participant. With custom channels, the Conversations API supports text messages.
Want to work with the native Email channel?
The Email Conversations API is an implementation of the Conversations API, designed specifically for Ada’s native Email channel. In this context, the same concepts apply, with a few differences for the native Email channel:
- Channel: You don’t create a new channel. Ada provides the native Email channel, and you interact with it via the Email Conversations API.
- Message: Messages are email-based (subject, body, optional cc/reply-as) and sent through the dedicated endpoint.
- Webhook support: Core lifecycle events (conversation started, message sent, conversation closed) are supported, but webhook coverage is more limited than for custom channels.
Talk to your AI Agent
Setup begins with a common step, then branches based on your use case.
- Generate an API key, if you don’t already have one.
- For custom channels, create a webhook and subscribe to conversation events. Then continue with the custom channel instructions.
- For conversations over Ada’s native Email channel, continue with the see Email channel instructions.
Conversations on custom channels
Use the Conversations API to create and run conversations over your own custom channels. The steps below show how to create a channel, start a conversation, exchange messages, and end the conversation programmatically.
1. Create a custom channel
Make sure you declare a modality so that the AI Agent responds to users in the corresponding style.
Request example
2. Create a conversation over your channel
If you have an existing end user, include their End User ID in the payload.
Otherwise, the Conversations API will make a new end user automatically. Make sure you save the End User ID from the response so you can send messages from this End User in the next step.
Important — Metadata ≠ Metavariables
The metadata object you send to create conversation does not create or set Ada metavariables. To create or update metavariables, use the End Users API.
When a conversation is successfully created, you’ll receive a v1.conversation.created webhook event if subscribed.
Request example
3. Send a message on behalf of the End User
Request example
When a message is successfully sent, you’ll receive a v1.conversation.message webhook event if subscribed. Note that the author.role will be end_user.
4. Listen for AI Agent response
When the AI Agent responds to your end user’s inquiry, you’ll receive a v1.conversation.message webhook event if subscribed. Note that the author.role will be ai_agent.
5. End a conversation on behalf of an end user
To end a conversation on behalf of the end user, call
Conversations on the native Email channel
How do you run conversations once you know the basics of the Email Conversations API for Ada’s native Email channel? Building on that foundation, you’ll configure a sender address, send conversations to Ada through the dedicated endpoint, and route replies for continuity.
For complete setup and implementation details, see this help topic.